The Future of AI in Agriculture: A Transformation in the Making
Imagine a world where crops tell you exactly what they need, where diseases are spotted before they spread, and robots work fields with tireless precision. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the future of farming driven by artificial intelligence (AI). AI isn’t just about futuristic gadgets; it’s about smarter use of resources, healthier harvests, and meeting the demands of our ever-growing world.

The Challenges Facing Modern Agriculture
Agriculture, the backbone of global food security, faces unprecedented challenges that threaten its capacity to feed the world:
Feeding a Growing World: Global population is projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050. This puts immense pressure on farmers to dramatically increase food production using the same (or even diminished) land resources.
Climate Change’s Toll: Droughts, floods, unpredictable weather, and shifting temperature zones are wreaking havoc on traditional farming. Crops fail, seasons become unreliable, and entire agricultural regions can be rendered unsuitable.
Resource Strain: Intensive agriculture can deplete vital resources. Water scarcity is a major threat, soil degradation is widespread, and fertilizer overuse contributes to pollution and environmental damage.
Labor Shortages: Agriculture often relies on a dwindling or migrant workforce. Finding sufficient skilled labor is a constant struggle, especially as the sector competes with other industries for workers.
Economic Pressures: Farmers face volatile markets, squeezed profit margins, and the rising costs of inputs like fertilizer and fuel. This instability makes farming a highly unpredictable and risky livelihood.
These interconnected challenges demand urgent solutions. To sustainably meet growing food needs, we must harness technological innovations, promote resilient farming practices, address climate change, and work towards more equitable global food systems.
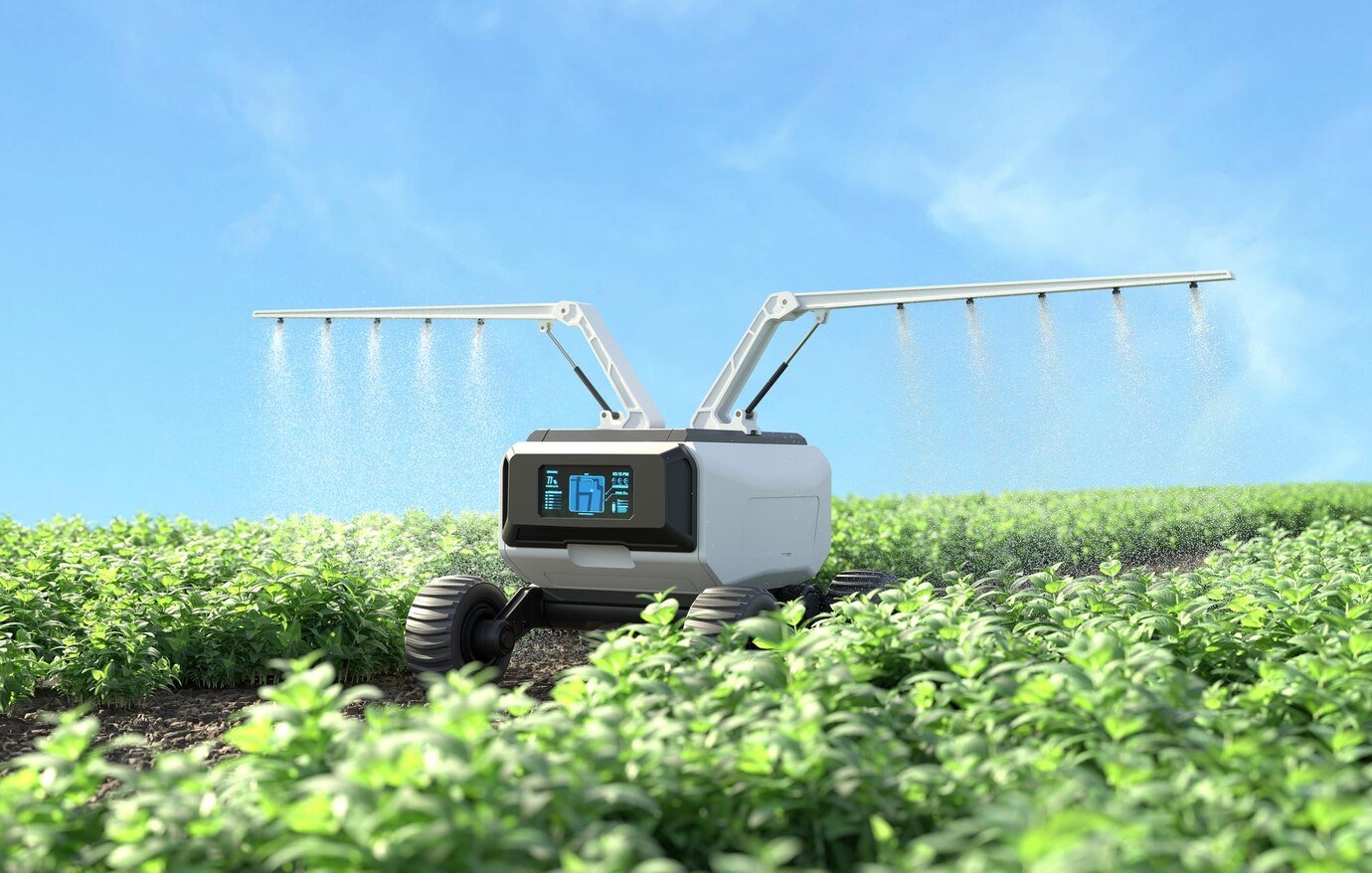


AI: The Game-Changing Technology for Agriculture
Farming has fed humanity for centuries, but the way we grow food is undergoing a radical change. AI (Artificial Intelligence) is stepping in with solutions to some of agriculture’s biggest problems.
Global population growth and climate change have placed immense pressure on farmers. They need to produce more food sustainably, with fewer resources. AI is the transformative technology we need.
Picture this: sensors in fields provide real-time data on soil moisture and nutrient levels. AI analyzes images to spot pests before they cause major damage. Weather data, combined with historical records, helps AI predict the perfect time to plant. Even robots powered by AI are coming to assist with tasks like weeding and harvesting.
These are just a few examples of AI’s potential in agriculture. The benefits are compelling:
- Precision Farming: AI-powered sensors and imaging systems can monitor crops with incredible detail. This enables farmers to pinpoint areas needing water, fertilizer, or pest treatment, optimizing resource usage and boosting yields.
- Disease and Pest Detection: AI algorithms can analyze plant images to identify diseases or pest infestations in the very early stages. This means farmers can take swift action, minimizing crop losses.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can combine weather data, soil conditions, historical yields, and more to predict optimal planting times, crop choices, and potential harvest outcomes. These forecasts help farmers make more informed decisions.
- Livestock Management: AI can track livestock behavior, health indicators, and feed intake. This level of monitoring can identify problems early, improving welfare, and even optimizing breeding.
- Autonomous Robots: Agricultural robots are a rapidly developing area. Powered by AI, they can perform tasks like weeding, harvesting delicate crops, and even applying targeted treatments with higher precision than traditional spraying
AI in agriculture is still rapidly evolving. Investment in cost-effective technology, gathering reliable data, and building trust among farmers are key to widespread adoption. However, the future is clear: AI-powered farms will be a major part of feeding our ever-growing world.


The Benefits of AI-Powered Farming
The challenge is clear: the world’s population is growing, and we need to drastically increase agricultural production to meet rising demands for food. Traditional farming methods, while resilient, are reaching their limits in the face of climate change and limited resources. Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform farming for the better, offering solutions that address both food security and environmental sustainability.
Enhanced Productivity
One of the most significant benefits of AI in agriculture is its ability to boost crop yields. AI-powered sensors and drones can provide farmers with unprecedented levels of detail about their fields. This data, analyzed by AI algorithms, translates into targeted recommendations on irrigation, fertilizer application, and pest control. By ensuring plants get exactly the resources they need, AI contributes directly to increased yields while minimizing wastage.
Prevention and Early Intervention
Crop diseases and pests are a constant threat to farmers. AI-powered image analysis tools can scan fields, even individual leaves, to identify signs of disease or infestation at incredibly early stages. This allows farmers to take rapid, targeted action before the problem spreads, saving significant portions of their crops.
Environmental Responsibility
AI’s focus on precision extends to resource management as a whole. By ensuring that water is delivered only where needed, and fertilizer or pesticides are applied with pinpoint accuracy, AI helps minimize agriculture’s environmental footprint. Additionally, AI can help develop more sustainable farming practices optimized for specific regional conditions.
Smarter Decision Making
Weather patterns, market prices, soil conditions – farmers manage a constant stream of complex variables. AI shines in turning this data overload into actionable insights. Predictive analytics powered by AI can inform farmers’ decisions regarding crop selection, optimal planting and harvesting times, and even predict market demand.
Robots to the Rescue
Labor shortages are a persistent challenge in agriculture. AI-powered robots are beginning to take on a range of tasks. From weeding and crop monitoring to delicate fruit picking, these robots bring tireless precision, freeing up human workers for more complex tasks and helping alleviate some of the labor pressures.
The Road to a Nourished Future
While the immense potential of AI in agriculture is clear, there is still a long way to go. Access to AI technology, the gathering of sufficient data, and farmer adoption present challenges. However, the benefits are so significant that AI-powered farming will likely become the backbone of providing food for a growing world, with increased output, improved food quality, and a lighter environmental touch shaping the future of how we feed ourselves


The Road Ahead: AI's Agricultural Revolution
The future of food production lies at the intersection of tradition and cutting-edge technology. Artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping agriculture as we know it. Precision sensors meticulously monitor fields, optimizing irrigation and pinpointing problem areas. AI algorithms swiftly identify the earliest signs of disease or pests, preventing widespread crop loss. Weather forecasts fused with historical data empower farmers with accurate predictions, guiding crucial decisions about planting and harvest.
This transformation isn’t without hurdles. High-tech solutions can be costly, and trust in AI decision-making takes time. Yet, the potential rewards are vast: greater yields meet the demands of a growing population, resources are used sustainably, and labor shortages are relieved by tireless robotic workers.
The road ahead for agriculture is one of both challenge and incredible promise. AI stands to nourish the world in ways never before possible, driving a more efficient, resilient, and abundant food supply for generations to come.
FAQs
A: AI’s ability to optimize resource use and increase yields will be transformative. Precision farming allows farmers to make incredibly targeted decisions about watering, fertilizer, and treatments, boosting production while reducing waste.
A: Yes! AI can analyze weather patterns and soil data to predict optimal planting times, ideal crop choices under changing conditions, and even prepare farmers for drought or extreme weather events.
A: While adoption might be slower, AI solutions are becoming more affordable and accessible. Shared data, community use of AI-powered tools, and government initiatives can make the technology available to farmers of all scales.
A: Machine learning, computer vision (image analysis), and predictive analytics are at the forefront, driving many AI-powered agricultural solutions.
A: Robots use computer vision to identify ripe fruits, weeds, or unhealthy plants. They also leverage AI for navigation, path planning, and advanced manipulation skills, enabling tasks like delicate harvesting or targeted treatment applications.
A: AI is more likely to change the nature of farm work rather than eliminate it entirely. Its strengths lie in automation of tedious tasks and precise data analysis, leaving room for human skill in decision-making and complex work.
A: It’s a valid concern. Initiatives focusing on data sharing, open-source AI models, and accessible AI education are crucial to ensure the benefits of AI technology are distributed equitably.












Pingback: Smarter Forests for a Greener Future: The Future of AI in Forestry - Meepri
Pingback: The Future of AI in Food and Beverage - Meepri
Pingback: The Future of AI in Textile and Apparel Manufacturing: A Revolution in the Making - Meepri
Pingback: The Future of AI in the Military: A Paradigm Shift in Warfare - Meepri
Pingback: What are the highest-paying AI jobs in the future: Top 5 Future Jobs. - Meepri
Pingback: The rise of artificial intelligence and its impact on society - Meepri
Pingback: AI in The Future Workplace: 10 Things to Know. - Meepri